
Unit 57 (Notes)
PHOTO AND EDITING
Composition (USE THIS WORD A LOT):
How its made up
Symmetrical composition
-
Composition
-
Rule of thirds
-
Parts of the picture which are focus and not in focus
-
Blurring on different parts of the picture
-
Lighting - exposure
-
Palette (USE THIS WORD WHEN TALKING ABOUT COLOURS!!!!)
Direct address to the audience (looking directly at the camera)
- When looking at the photo, it seems the person in the photo is looking at you
Negative space (Empty space)
Leading lines
Depth of field (Where it is blurred)
Monochrome (Black and White)
If you want to blur out the background, the foreground has to be in focus!
Repetition (lines of symmetry? Patterns?)
Cropping photo’s (getting what you want in the frame)
Problems with photo’s to look out for:
-
Over exposed
-
Doesn’t show much colour (ie. pearl white background becomes pure white (Loss of colour))
-
Lighting
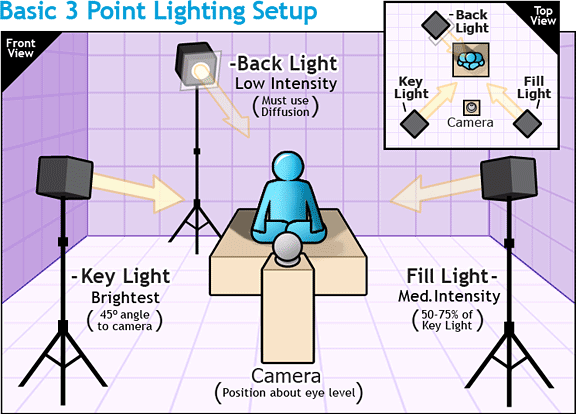
3 point lighting
- Key Light (Main light (normally the brightest))
- Fill Light (Second light (second light that is the brightet))
- Back Light (Thirst light (normally the light that is the dimest))
2 tpypes of light systems
Zy-light
- When the light is warm, the colour is an orangey colour
- Whent the light is warm, the temperature of the light is around 2000℃
- When the light is cold, the colour is either white or a blue colour
- When the light is cold, the temprature of the light is around 10000℃
- The temperature of the lights are around 2000℃ - 10000℃
Kino lights
- Normally are the back lights
- These are used to brighten or touch up some colours on the back or top of the head
Camera
DSLR - Digital Sing Lens R
The better the camera, the better sensor in the camera
There are mirrors in the camera
When taking a picture, the 'clunk' sound is the hole that closes to take a picture
ISO - Changing the sensitivity of the sensor in the camera (ie ISO 100)
- When it is more sensitive the grain look they get
- Best when the ISO is low
Shutter speed - fractions of a second to take a picture
- Normally presented in a fraction (ie. 1/125)
Aperature (F stop)
- Changes the size of the hole
- The bigger the number, the smaller the hole (ie f/2.8 is smaller than f/2.2)
Changing the exposure depends on brightening it or darkening it
-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3
AWB - Auto White Balance
Prime lens
- Cannot zoom in
50mm - Close shots
- Narrow focus
- Boka - Background blur
10-18mm - For wide shots
18 - 55mm -
LENS
Focal Length - The distance between the sensor and the point of convergence
From the lens on the camera light shines in through the glass, distorts the light.
Light then goes to the pint of convergence which reflect the light to the sensor.
- Prime lens
- Zoom lens
Sometimes affects the depth of field
Distance between things
Depends on the type of lens you have
CD Cover
Abstract/expressional
Pareto
Principle
| Zero is the perfect exposure (Depends)
Notes for my camera:
Nikon D5000
35mm 1.8 dx nikon (lens)